| Type: | Package |
| Title: | Reproducible Color Characterization of Digital Images for Biological Studies |
| Version: | 1.0.0 |
| Description: | Provides a standardized and reproducible framework for characterizing and classifying discrete color classes from digital images of biological organisms. The package automatically determines the presence or absence of 10 human-visible color categories (black, blue, brown, green, grey, orange, purple, red, white, yellow) using a biologically-inspired Color Look-Up Table (CLUT) that partitions HSV color space. Supports both fully automated and semi-automated (interactive) workflows with complete provenance tracking for reproducibility. Pre-processes images using the 'recolorize' package (Weller et al. 2024 <doi:10.1111/ele.14378>) for spatial-color binning, and integrates with 'pavo' (Maia et al. 2019 <doi:10.1111/2041-210X.13174>) for color pattern geometry statistics. Designed for high-throughput analysis and seamless integration with downstream evolutionary analyses. |
| License: | MIT + file LICENSE |
| URL: | https://github.com/shawntz/charisma, https://shawnschwartz.com/charisma/ |
| BugReports: | https://github.com/shawntz/charisma/issues |
| Encoding: | UTF-8 |
| LazyData: | true |
| Depends: | R (≥ 4.0.0) |
| Imports: | magrittr, plyr, dplyr, tibble, purrr, tidyr, parallel, recolorize, imager, abind, jpeg, png, grDevices, graphics, stats, tools, utils |
| Suggests: | pavo, testthat (≥ 3.0.0), knitr, rmarkdown, pkgdown |
| VignetteBuilder: | knitr |
| RoxygenNote: | 7.3.3 |
| Config/testthat/edition: | 3 |
| NeedsCompilation: | no |
| Packaged: | 2025-12-01 18:21:00 UTC; shawn.schwartz |
| Author: | Shawn Schwartz |
| Maintainer: | Shawn Schwartz <shawn.t.schwartz@gmail.com> |
| Repository: | CRAN |
| Date/Publication: | 2025-12-08 08:20:22 UTC |
charisma: Reproducible Color Characterization of Digital Images for Biological Studies
Description

Provides a standardized and reproducible framework for characterizing and classifying discrete color classes from digital images of biological organisms. The package automatically determines the presence or absence of 10 human-visible color categories (black, blue, brown, green, grey, orange, purple, red, white, yellow) using a biologically-inspired Color Look-Up Table (CLUT) that partitions HSV color space. Supports both fully automated and semi-automated (interactive) workflows with complete provenance tracking for reproducibility. Pre-processes images using the 'recolorize' package (Weller et al. 2024 doi:10.1111/ele.14378) for spatial-color binning, and integrates with 'pavo' (Maia et al. 2019 doi:10.1111/2041-210X.13174) for color pattern geometry statistics. Designed for high-throughput analysis and seamless integration with downstream evolutionary analyses.
Author(s)
Maintainer: Shawn Schwartz shawn.t.schwartz@gmail.com (ORCID) [copyright holder]
Authors:
Whitney Tsai wtsai@nhm.org (ORCID)
Elizabeth Karan (ORCID)
Mark Juhn
Allison Shultz ashultz@nhm.org (ORCID)
John McCormack (ORCID)
Thomas Smith (ORCID)
Michael Alfaro michaelalfaro@g.ucla.edu (ORCID)
See Also
Useful links:
Report bugs at https://github.com/shawntz/charisma/issues
Characterize color classes in biological images
Description
The primary function of charisma is to characterize the distribution
of human-visible color classes present in an image. This function provides
a standardized and reproducible framework for classifying colors into
discrete categories using a biologically-inspired Color Look-Up Table (CLUT).
Usage
charisma(
img_path,
threshold = 0,
auto.drop = TRUE,
interactive = FALSE,
plot = FALSE,
pavo = TRUE,
logdir = NULL,
stack_colors = TRUE,
bins = 4,
cutoff = 20,
k.override = NULL,
clut = charisma::clut
)
Arguments
img_path |
Character string specifying the path to an image file, or a
|
threshold |
Numeric value between 0 and 1 specifying the minimum proportion of pixels required for a color to be retained. Colors with proportions below this threshold are automatically removed. Default is 0.0 (retain all colors). |
auto.drop |
Logical. If |
interactive |
Logical. If |
plot |
Logical. If |
pavo |
Logical. If |
logdir |
Character string specifying the directory path for saving
output files. If provided, saves timestamped .RDS (charisma object) and
.PDF (diagnostic plots) files. Default is |
stack_colors |
Logical. If |
bins |
Integer specifying the number of bins for each RGB channel in the histogram method. Default is 4 (resulting in 4^3 = 64 cluster centers). |
cutoff |
Numeric value specifying the Euclidean distance threshold for combining similar color clusters. Default is 20. |
k.override |
Integer to force a specific number of color clusters,
bypassing automatic detection. Default is |
clut |
Data frame containing the Color Look-Up Table with HSV boundaries
for each color class. Default is |
Details
The charisma pipeline consists of three main stages:
-
Image preprocessing: Uses
recolorize::recolorize2()to perform spatial-color binning, removing noisy pixels and creating a smoothed representation of dominant colors. -
Color classification: Converts RGB cluster centers to HSV color space and matches them against non-overlapping HSV ranges defined in the CLUT using
charisma::color2label(). -
Optional manual curation: In interactive mode, users can merge color clusters (e.g., c(2,3)) or replace pixels between clusters to refine classifications.
The workflow can be run fully autonomously or with varying degrees of manual intervention. All operations are logged for complete reproducibility.
Value
A charisma object (list) containing:
centers |
RGB cluster centers |
pixel_assignments |
Pixel-to-cluster mapping |
classification |
Discrete color labels from CLUT |
color_mask_LUT |
Mapping of clusters to averaged colors |
color_mask_LUT_filtered |
Color mapping after threshold applied |
merge_history |
Record of all merge operations performed |
replacement_history |
Record of all replacement operations performed |
merge_states |
List of charisma states after each merge |
replacement_states |
List of charisma states after each replacement |
pavo_stats |
Color pattern geometry metrics (if pavo = TRUE) |
prop_threshold |
Threshold value used |
path |
Path to original image |
logdir |
Directory where outputs were saved |
auto_drop |
Value of auto.drop parameter |
bins |
Value of bins parameter |
cutoff |
Value of cutoff parameter |
clut |
CLUT used for classification |
stack_colors |
Value of stack_colors parameter |
References
Schwartz, S.T., Tsai, W.L.E., Karan, E.A., Juhn, M.S., Shultz, A.J., McCormack, J.E., Smith, T.B., and Alfaro, M.E. (2025). charisma: An R package to perform reproducible color characterization of digital images for biological studies. (In Review).
Weller, H.I., Hiller, A.E., Lord, N.P., and Van Belleghem, S.M. (2024). recolorize: An R package for flexible colour segmentation of biological images. Ecology Letters, 27(2):e14378.
See Also
charisma2 for re-analyzing saved charisma objects,
color2label for RGB to color label conversion,
validate for CLUT validation,
plot.charisma for visualization
Examples
# Basic usage with example image
img <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa_LACM60421.png",
package = "charisma")
result <- charisma(img)
# With threshold to remove minor colors
result <- charisma(img, threshold = 0.05)
# Save outputs to directory
out_dir <- file.path(tempdir(), "charisma_outputs")
result <- charisma(img, threshold = 0.05, logdir = out_dir)
# View results
plot(result)
# Interactive mode with manual curation (only runs in interactive sessions)
if (interactive()) {
img <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa_LACM60421.png",
package = "charisma")
result <- charisma(img, interactive = TRUE, threshold = 0.0)
}
Re-analyze and edit saved charisma objects
Description
The charisma2 function allows users to step through and edit
previously saved charisma objects. This function enables rewinding
to specific merge or replacement states, applying different thresholds, or
continuing interactive editing from any saved state, ensuring full
reproducibility of the analysis.
Usage
charisma2(
charisma.obj,
interactive = TRUE,
new.threshold = NULL,
which.state = c("none", "merge", "replace"),
state.index = NULL,
k.override = NULL
)
Arguments
charisma.obj |
A |
interactive |
Logical. If |
new.threshold |
Numeric value between 0 and 1 to apply a different color
proportion threshold than the original analysis. If |
which.state |
Character string specifying which state to revert to.
Options are |
state.index |
Integer specifying which state index to revert to when
|
k.override |
Integer to force a specific number of color clusters.
Default is |
Details
The charisma2 function provides powerful state management
capabilities:
-
State rewinding: Jump to any previous merge or replacement state
-
Re-thresholding: Apply different color proportion thresholds without re-running the entire pipeline
-
Continued editing: Resume interactive editing from saved states
-
Full provenance: All operations maintain complete history for reproducibility
Note: Interactive adjustment of merge states is disabled if replacement states exist, as replacement operations depend on post-merge cluster indices.
Value
A charisma2 object (also of class charisma) containing
the same structure as a charisma object, with updated states based
on the specified reversion point and any new operations performed.
References
Schwartz, S.T., Tsai, W.L.E., Karan, E.A., Juhn, M.S., Shultz, A.J., McCormack, J.E., Smith, T.B., and Alfaro, M.E. (2025). charisma: An R package to perform reproducible color characterization of digital images for biological studies. (In Review).
See Also
charisma for initial color classification,
plot.charisma for visualization
Examples
# Load a previously saved charisma object
obj <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa.RDS", package = "charisma")
obj <- readRDS(obj)
## Not run:
# Examples that require objects with merge/replacement states
# (These examples show the syntax but won't run with the provided test data)
# Revert to a specific merge state (if merge states exist)
if (length(obj$merge_states) >= 2) {
result <- charisma2(obj, which.state = "merge", state.index = 2)
}
# Revert to a specific replacement state (if replacement states exist)
if (length(obj$replacement_states) >= 1) {
result <- charisma2(obj, which.state = "replace", state.index = 1)
}
# Re-enter interactive mode with original threshold
obj <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa.RDS", package = "charisma")
obj <- readRDS(obj)
result <- charisma2(obj, interactive = TRUE)
## End(Not run)
Default Color (Labels) Look Up Table (CLUT)
Description
This LUT contains all color boundaries which cut up the continuous HSV color space into 10 discrete color labels (i.e., black, white, grey, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and purple).
Usage
clut
Format
A data frame with color boundary definitions for HSV color space. Each row defines the HSV ranges for a specific discrete color category.
Details
These color boundaries were determined by forming consensus across three experts in the biology of color. Color boundaries were intentionally tuned to reflect accurate color label classifications for images of various bird and fish museum specimens.
Although we attempted to determine color boundaries in an object fashion, there are of course perceptual biases and variability across computer models/ displays that can influence whether any given color at the boundary of the continuous color space is ultimately called one color over another.
Accordingly, we gladly welcome further optimization of the default color LUT
and/or submissions of color LUTS specifically tuned to any given organism or
stimulus. Leveraging contributions from the community will only help
charisma be more useful for everybody who would like to use it!
See Also
charisma for the main classification pipeline,
validate for CLUT validation
Examples
# View the default CLUT
head(clut)
Convert RGB color triplets to discrete color labels
Description
This function classifies an RGB color triplet into one of the discrete color categories defined in the Color Look-Up Table (CLUT) by testing for membership within non-overlapping HSV ranges.
Usage
color2label(color_triplet, verbose = FALSE, clut = charisma::clut)
Arguments
color_triplet |
Numeric vector of length 3 containing RGB values (0-255 scale). The vector should be c(red, green, blue). |
verbose |
Logical. If |
clut |
Data frame containing the Color Look-Up Table with HSV boundaries
for each color class. Default is |
Details
The classification process involves:
Converting RGB to HSV (using
rgb2hsv)Scaling HSV to match CLUT ranges (H: 0-360, S: 0-100, V: 0-100)
Testing the HSV coordinate against all color definitions in the CLUT
Returning the single matching color label
Each color in the CLUT has non-overlapping HSV ranges that partition the entire HSV color space. If multiple matches occur, a warning is issued as this indicates overlapping color boundaries in the CLUT.
Value
Character string indicating the matched color label from the CLUT.
Returns "NA" if the input contains NA values.
References
Schwartz, S.T., Tsai, W.L.E., Karan, E.A., Juhn, M.S., Shultz, A.J., McCormack, J.E., Smith, T.B., and Alfaro, M.E. (2025). charisma: An R package to perform reproducible color characterization of digital images for biological studies. (In Review).
See Also
charisma for the main classification pipeline,
validate for CLUT validation
Examples
# Classify a blue RGB color
color2label(c(0, 0, 255))
# Classify a red RGB color
color2label(c(255, 0, 0))
# Verbose output for debugging
color2label(c(128, 128, 128), verbose = TRUE)
Change colors of dendrogram tips
Description
Internal function for recolorize::recluster plotting.
Usage
labelCol(x, hex_cols, pch = 20, cex = 2)
Arguments
x |
Leaf of a dendrogram. |
hex_cols |
Hex color codes for colors to change to. |
pch |
The type of point to draw. |
cex |
The size of the point. |
Value
An hclust object with colored tips.
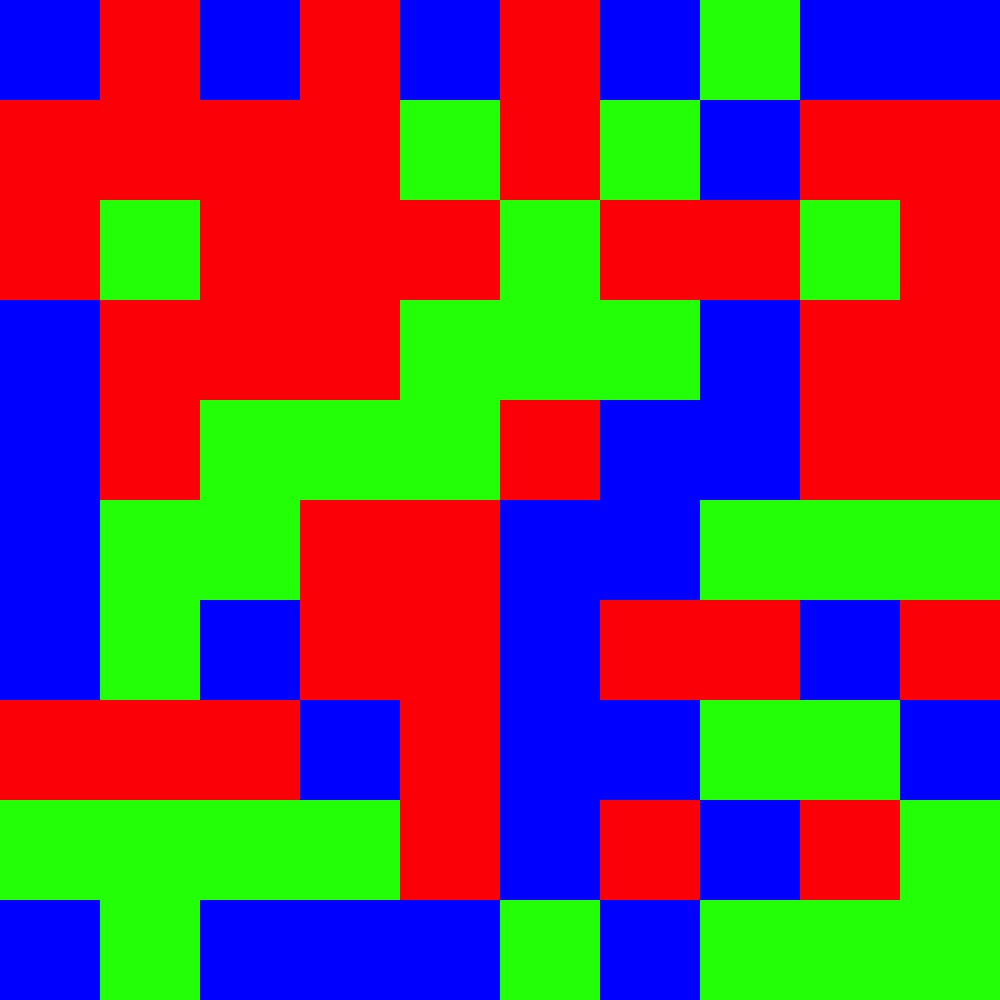
Create a color mosaic visualization from color proportions
Description
This function generates a randomized mosaic grid visualization representing the proportions of different colors, useful for visually displaying color composition in a standardized format.
Usage
mosaic(
color.props,
size = 10,
out.path = normalizePath("~"),
out.prefix = "charisma_mosaic",
verbose = TRUE
)
Arguments
color.props |
List of color proportion objects, where each element contains:
|
size |
Integer specifying the dimensions of the mosaic grid (size x size). Default is 10 (resulting in a 10 x 10 = 100 cell mosaic). |
out.path |
Character string specifying the directory path for saving the output PNG file. Default is the user's home directory. |
out.prefix |
Character string prefix for the output filename. Default is
|
verbose |
Logical. If |
Details
The mosaic function creates a visual representation of color proportions by:
Allocating grid cells proportional to each color's proportion
Randomly shuffling cell positions to create a mosaic pattern
Saving the result as a PNG file with an informative filename
The output filename automatically encodes the hex codes, color names, and proportions for documentation purposes.
Value
Character string containing the full path to the saved PNG file.
See Also
charisma for generating color classifications
Examples
# Create a mosaic from color proportions
colors <- list(
list(hex = "#FF0000", color = "red", prop = 0.4),
list(hex = "#00FF00", color = "green", prop = 0.3),
list(hex = "#0000FF", color = "blue", prop = 0.3)
)
mosaic(colors, size = 10, out.path = tempdir())
Plot method for charisma objects
Description
This function creates visualizations of color classification results from a charisma analysis. It can display the original image, recolored image, masked image, color proportions, and pavo color pattern geometry results.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'charisma'
plot(
x,
plot.all = TRUE,
plot.original = FALSE,
plot.recolored = FALSE,
plot.masked = FALSE,
plot.props = FALSE,
plot.pavo.img = FALSE,
plot.pavo.classes = FALSE,
font.size = 1.75,
props.x.cex = 1.5,
real.bar.colors = TRUE,
...
)
Arguments
x |
|
plot.all |
Logical. If |
plot.original |
Logical. If |
plot.recolored |
Logical. If |
plot.masked |
Logical. If |
plot.props |
Logical. If |
plot.pavo.img |
Logical. If |
plot.pavo.classes |
Logical. If |
font.size |
Numeric. Size multiplier for plot text elements. Default
is |
props.x.cex |
Numeric. Size multiplier for x-axis labels in the
proportions plot. Default is |
real.bar.colors |
Logical. If |
... |
Additional arguments (currently not used). |
Details
When plot.all = TRUE, all available plots are displayed in a
multi-panel layout. Individual plots can be selected by setting the
corresponding plot.* parameters to TRUE.
The function automatically detects whether pavo analysis results are present in the charisma object and adjusts the plot layout accordingly.
Value
This function is called for its side effects (creating plots) and does not return a value.
See Also
charisma for the main classification pipeline,
charisma2 for batch processing
Examples
# Run charisma on an image
img <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa_LACM60421.png",
package = "charisma")
result <- charisma(img)
# Plot all results
plot(result)
# Plot only original and recolored images
plot(result, plot.all = FALSE, plot.original = TRUE, plot.recolored = TRUE)
# Plot color proportions
plot(result, plot.all = FALSE, plot.props = TRUE)
Summarize color classification results
Description
This function takes a charisma object and produces a summary table showing the proportion of pixels classified into each discrete color category.
Usage
summarize(charisma_obj)
summarise(charisma_obj)
Arguments
charisma_obj |
A charisma object (output from |
Details
The summary table shows the percentage of pixels classified into each of the discrete color categories defined in the Color Look-Up Table (CLUT). This provides a quantitative overview of the color composition of the analyzed image.
Value
A data frame with one row per image showing the proportion of pixels assigned to each color category. Row names are set to the basename of the image file path.
See Also
charisma for the main classification pipeline,
validate for CLUT validation
Examples
# Run charisma on an image
img <- system.file("extdata", "Tangara_fastuosa_LACM60421.png",
package = "charisma")
result <- charisma(img)
# Summarize the color classification results
summary_table <- summarize(result)
print(summary_table)
Validate Color Look-Up Table completeness
Description
This function validates that a Color Look-Up Table (CLUT) provides complete and non-overlapping coverage of the HSV color space by testing every HSV coordinate against the CLUT definitions. Validation ensures each color maps to exactly one color class.
Usage
validate(clut = charisma::clut, simple = TRUE)
Arguments
clut |
Data frame containing the Color Look-Up Table with HSV boundaries
for each color class. Default is |
simple |
Logical. If |
Details
The validation process:
Generates a complete grid of HSV color space coordinates
Uses parallel processing (all available cores - 1) to classify each coordinate using the CLUT definitions
Checks that each coordinate maps to exactly one color class
Reports any missing or duplicate classifications
Validation is essential when modifying the CLUT or creating custom CLUTs for
different image datasets. The process can take several minutes even with
simple = TRUE.
Value
If validation passes, returns 0 and prints a success message. If validation fails, returns a data frame containing all HSV coordinates that either: (1) were not classified to any color, or (2) were classified to multiple colors (indicating overlap).
References
Schwartz, S.T., Tsai, W.L.E., Karan, E.A., Juhn, M.S., Shultz, A.J., McCormack, J.E., Smith, T.B., and Alfaro, M.E. (2025). charisma: An R package to perform reproducible color characterization of digital images for biological studies. (In Review).
See Also
charisma for using validated CLUTs,
color2label for color classification
Examples
## Not run:
# Validate the default CLUT (takes several minutes with parallel processing)
# Note: These examples are not run during R CMD check due to CRAN build
# limitations. With only 2 cores available during CRAN checks, validation
# can exceed 20 minutes.
result <- validate()
# Validate a custom CLUT
my_clut <- charisma::clut # Start with default
# ... modify my_clut ...
result <- validate(clut = my_clut)
# More thorough validation (much slower, recommended for cluster computing)
result <- validate(simple = FALSE)
## End(Not run)